Page 30 - Practical Approaches to Managing Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC)
P. 30
®
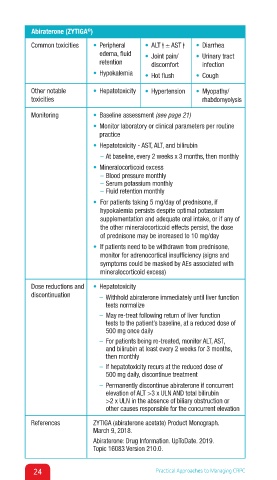
Abiraterone (ZYTIGA )
Common toxicities • Peripheral • ALT ↑ ± AST ↑ • Diarrhea ↑
edema, fluid • Joint pain/ • Urinary tract
retention discomfort infection
• Hypokalemia • Hot flush • Cough
Other notable • Hepatotoxicity • Hypertension • Myopathy/
toxicities rhabdomyolysis
Monitoring • Baseline assessment (see page 21)
• Monitor laboratory or clinical parameters per routine
practice
• Hepatotoxicity - AST, ALT, and bilirubin
– At baseline, every 2 weeks x 3 months, then monthly
• Mineralocorticoid excess
– Blood pressure monthly
– Serum potassium monthly
– Fluid retention monthly
• For patients taking 5 mg/day of prednisone, if
hypokalemia persists despite optimal potassium
supplementation and adequate oral intake, or if any of
the other mineralocorticoid effects persist, the dose
of prednisone may be increased to 10 mg/day
• If patients need to be withdrawn from prednisone,
monitor for adrenocortical insufficiency (signs and
symptoms could be masked by AEs associated with
mineralocorticoid excess)
Dose reductions and • Hepatotoxicity
discontinuation – Withhold abiraterone immediately until liver function
tests normalize
– May re-treat following return of liver function
tests to the patient’s baseline, at a reduced dose of
500 mg once daily
– For patients being re-treated, monitor ALT, AST,
and bilirubin at least every 2 weeks for 3 months,
then monthly
– If hepatotoxicity recurs at the reduced dose of
500 mg daily, discontinue treatment
– Permanently discontinue abiraterone if concurrent
elevation of ALT >3 x ULN AND total bilirubin
>2 x ULN in the absence of biliary obstruction or
other causes responsible for the concurrent elevation
References ZYTIGA (abiraterone acetate) Product Monograph.
March 9, 2018.
Abiraterone: Drug Information. UpToDate. 2019.
Topic 16083 Version 210.0.
24 Practical Approaches to Managing CRPC