Page 32 - Practical Approaches to Managing Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC)
P. 32
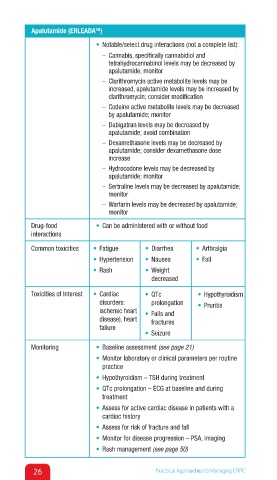
Apalutamide (ERLEADA )
TM
• Notable/select drug interactions (not a complete list):
– Cannabis, specifically cannabidiol and
tetrahydrocannabinol levels may be decreased by
apalutamide; monitor
– Clarithromycin active metabolite levels may be
increased, apalutamide levels may be increased by
clarithromycin; consider modification
– Codeine active metabolite levels may be decreased
by apalutamide; monitor
– Dabigatran levels may be decreased by
apalutamide; avoid combination
– Dexamethasone levels may be decreased by
apalutamide; consider dexamethasone dose
increase
– Hydrocodone levels may be decreased by
apalutamide; monitor
– Sertraline levels may be decreased by apalutamide;
monitor
– Warfarin levels may be decreased by apalutamide;
monitor
Drug-food • Can be administered with or without food
interactions
Common toxicities • Fatigue • Diarrhea ↑ • Arthralgia↑
• Hypertension • Nausea • Fall
• Rash • Weight
decreased
Toxicities of Interest • Cardiac • QTc • Hypothyroidism
disorders: prolongation • Pruritis
ischemic heart • Falls and
disease), heart fractures
failure
• Seizure
Monitoring • Baseline assessment (see page 21)
• Monitor laboratory or clinical parameters per routine
practice
• Hypothyroidism – TSH during treatment
• QTc prolongation – ECG at baseline and during
treatment
• Assess for active cardiac disease in patients with a
cardiac history
• Assess for risk of fracture and fall
• Monitor for disease progression – PSA, imaging
• Rash management (see page 50)
26 Practical Approaches to Managing CRPC